Unveiling the Hidden World of Parasites in Social Insects: A Comprehensive Guide

Social insects, such as ants, termites, bees, and wasps, live in complex and fascinating societies. These highly organized colonies provide a fertile ground for a diverse array of organisms, including parasites. Parasites are organisms that live on or in a host organism and obtain nutrients from it. In social insects, parasites can have a profound impact on the behavior, ecology, and evolution of their hosts.
4.3 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44882 KB |
| Print length | : | 392 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
This article delves into the intriguing and complex world of parasites in social insects. We will explore the different types of parasites, their intricate relationships with their hosts, and the profound effects they have on insect societies. This comprehensive guide will provide a deeper understanding of the hidden interactions that shape the lives of these remarkable creatures.
Types of Parasites in Social Insects
Parasites in social insects come in a wide range of forms, each with unique adaptations for exploiting their hosts. Some of the most common types of parasites include:
- Protozoans: Single-celled organisms that can infect the digestive system, circulatory system, or other tissues of their hosts.
- Bacteria: Microscopic organisms that can cause diseases or disrupt normal host physiology.
- Fungi: Organisms that can grow on the exoskeleton or inside the bodies of their hosts, causing damage or nutrient depletion.
- Viruses: Infectious agents that can replicate within host cells, causing a range of symptoms.
- Nematodes: Roundworms that can live in the digestive tract or other tissues of their hosts.
- Ectoparasites: Parasites that live on the external surfaces of their hosts, such as mites, ticks, and lice.
Host-Parasite Interactions
The interactions between parasites and social insects are complex and dynamic. Some parasites have evolved to have a minimal impact on their hosts, while others can be highly virulent, causing significant harm or even death. The nature of the host-parasite interaction depends on a variety of factors, including the parasite's life cycle, the host's immune system, and the social structure of the colony.
In some cases, parasites can benefit their hosts. For example, some protozoans in termites help their hosts digest cellulose, which is essential for their survival. However, most parasites have a negative impact on their hosts, reducing their fitness, reproductive success, or lifespan.
Effects on Insect Societies
Parasites can have a profound impact on the structure and function of social insect colonies. High levels of parasitism can lead to:
- Reduced colony size: Parasites can kill or weaken individual insects, leading to a decline in colony population.
- Altered social behavior: Parasites can disrupt the normal communication and cooperation among colony members.
- Increased susceptibility to other threats: Parasites can weaken insect immune systems, making colonies more vulnerable to predators, pathogens, and environmental stressors.
- Evolutionary adaptations: Over time, social insects have evolved a variety of defenses against parasites, such as hygienic behaviors, social distancing, and antimicrobial compounds.
Case Studies: Parasites in Ants, Termites, Bees, and Wasps
To illustrate the diversity and impact of parasites in social insects, let's explore some specific case studies:
Parasites in Ants
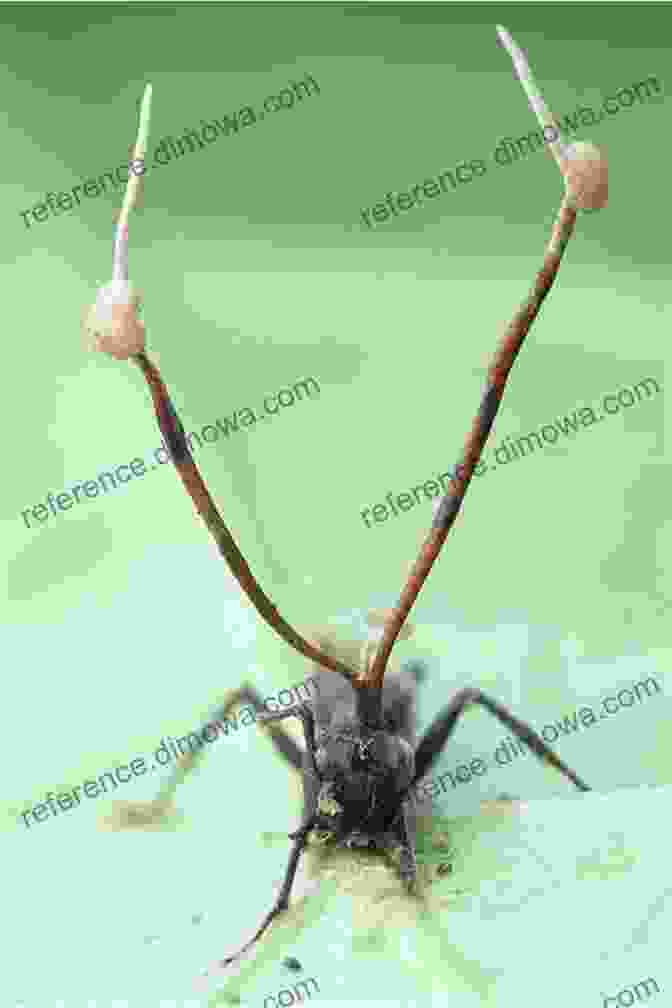

Ants are hosts to a wide range of parasites, including protozoans, fungi, bacteria, and nematodes. One of the most fascinating examples is the fungus Ophiocordyceps unilateralis, which infects carpenter ants. The fungus takes control of the ant's behavior, forcing it to climb to the top of a plant and attach itself to a leaf. The fungus then grows out of the ant's head, releasing spores that infect other ants.
Parasites in Termites
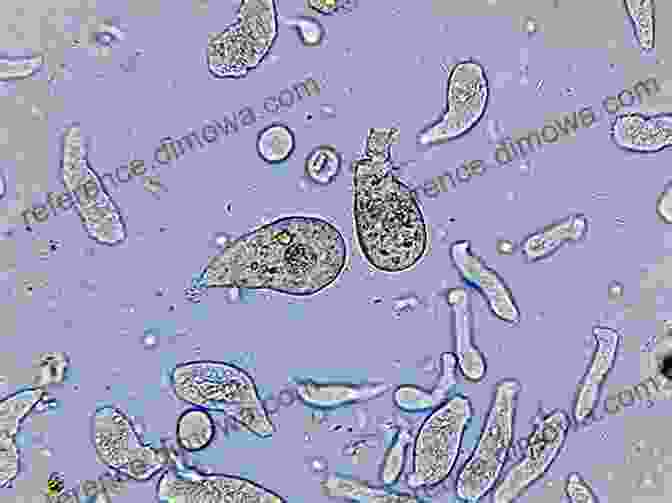
Termites are also hosts to a variety of parasites, including protozoans, bacteria, and viruses. One of the most common parasites is the protozoan Trichonympha, which lives in the termite's digestive system and helps it digest cellulose. However, some strains of Trichonympha can become pathogenic, causing the termite to lose weight and become more susceptible to other infections.
Parasites in Bees
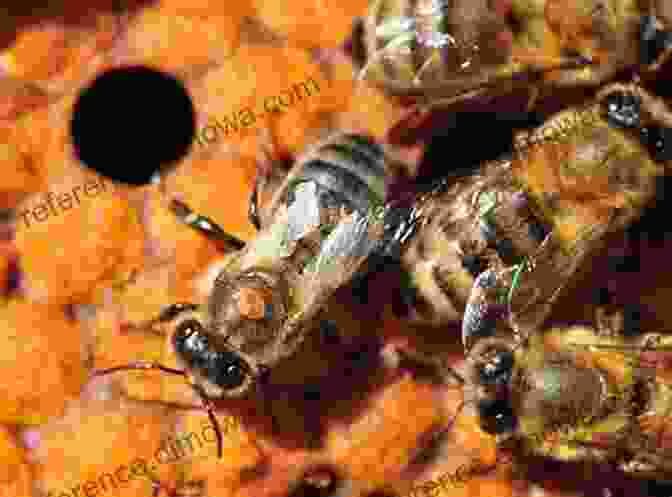

Bees are hosts to a range of parasites, including mites, viruses, and bacteria. One of the most devastating parasites is the Varroa destructor mite, which feeds on the blood of honeybees. Heavy infestations of Varroa mites can weaken bees, reduce honey production, and spread viruses throughout the colony.
Parasites in Wasps
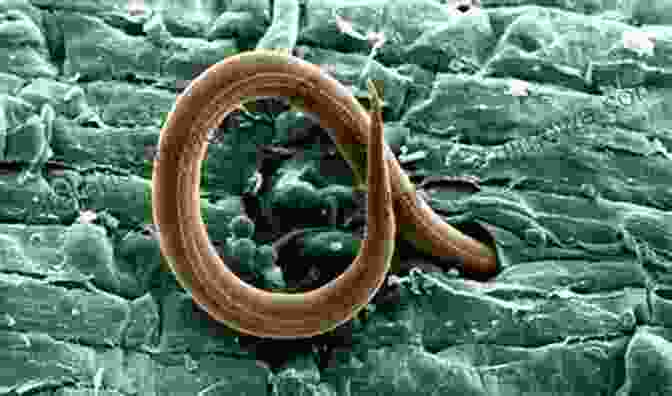
Wasps are hosts to a range of parasites, including protozoans, fungi, and nematodes. One of the most common parasites is the nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora, which infects
4.3 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44882 KB |
| Print length | : | 392 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia William W Lace
William W Lace Gil Fried
Gil Fried Masahiro Hikokubo
Masahiro Hikokubo Matthew Vale
Matthew Vale Jamey Hecht
Jamey Hecht Glen D Gillen
Glen D Gillen Aaron Michael Ritchey
Aaron Michael Ritchey A L Tate
A L Tate Michael Rutter
Michael Rutter Andria Buchanan
Andria Buchanan Jerald E Pinto
Jerald E Pinto Jason Born
Jason Born Abigail Rutherford
Abigail Rutherford Nigel Cleere
Nigel Cleere Mike Aylwin
Mike Aylwin Erwin Rosen
Erwin Rosen Julian Reiss
Julian Reiss Abigail Cutter
Abigail Cutter David S Favre
David S Favre John Keegan
John Keegan
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 W. Somerset MaughamJane Eyre by Chloe Hubert: An Unforgettable Gothic Romance for the Ages
W. Somerset MaughamJane Eyre by Chloe Hubert: An Unforgettable Gothic Romance for the Ages
 Miguel de CervantesImmerse Yourself in a Captivating Historical Western Romance: Christmas...
Miguel de CervantesImmerse Yourself in a Captivating Historical Western Romance: Christmas... Jack PowellFollow ·18.6k
Jack PowellFollow ·18.6k Drew BellFollow ·4k
Drew BellFollow ·4k Daniel KnightFollow ·15.3k
Daniel KnightFollow ·15.3k Ernest HemingwayFollow ·7.2k
Ernest HemingwayFollow ·7.2k Duane KellyFollow ·7.6k
Duane KellyFollow ·7.6k Jonathan HayesFollow ·11.4k
Jonathan HayesFollow ·11.4k Jeremy CookFollow ·15.7k
Jeremy CookFollow ·15.7k Marc FosterFollow ·4.4k
Marc FosterFollow ·4.4k

 Julio Cortázar
Julio CortázarShift Your Perspective, Seize Your Potential, Own Your...
A Transformative Guide to...

 Isaias Blair
Isaias BlairPractical Algorithms For 3d Computer Graphics: Unlocking...
In the realm of digital artistry, 3D computer...

 Joseph Heller
Joseph HellerClear Vision Through Cloudy Eyes: A Guide to Overcoming...
Have you ever felt...

 Leo Tolstoy
Leo TolstoyThe True Story of My Fairygodparent Who Almost Killed Me...
Book Description In this captivating...

 Earl Williams
Earl WilliamsCanada 10 Must Visit Locations: A Captivating Journey...
Prologue: A...
4.3 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 44882 KB |
| Print length | : | 392 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |